Nigeria with a population of over 193 million people (The World Bank Group, 2018), HIV/AIDS remains a growing public health issue. The people living with the virus are about 1.9 million [UNAIDS Press release, 2019] and it is observed that there is an increase of new infection among adolescents and young people. Existing research results show that in Nigeria, adolescents and young people, aged 20–24 have a higher prevalence of 3.2%. Moreover, young people aged 15–19 had a prevalence of 2.9% [Ezenekwe, et al, 2018].
What is iTest
iTest is a collaborative research and development project between CcHUB, Nigeria Institute of Medical Research (NIMR) and the 4 Youth By Youth (4yBy) team. The goal of the project is to create a system that supports HIV self-testing in Nigeria by collecting test-related data and linking potential patients to care. As part of the project, community outreach was carried out in various parts of Lagos state. The goal was to help young people between ages 15-24 years in Lagos carry out free HIV self-tests while also taking a risk assessment quiz to determine their level of risk of contracting HIV.
Results of data collected during the outreach
Submission
Prevalence
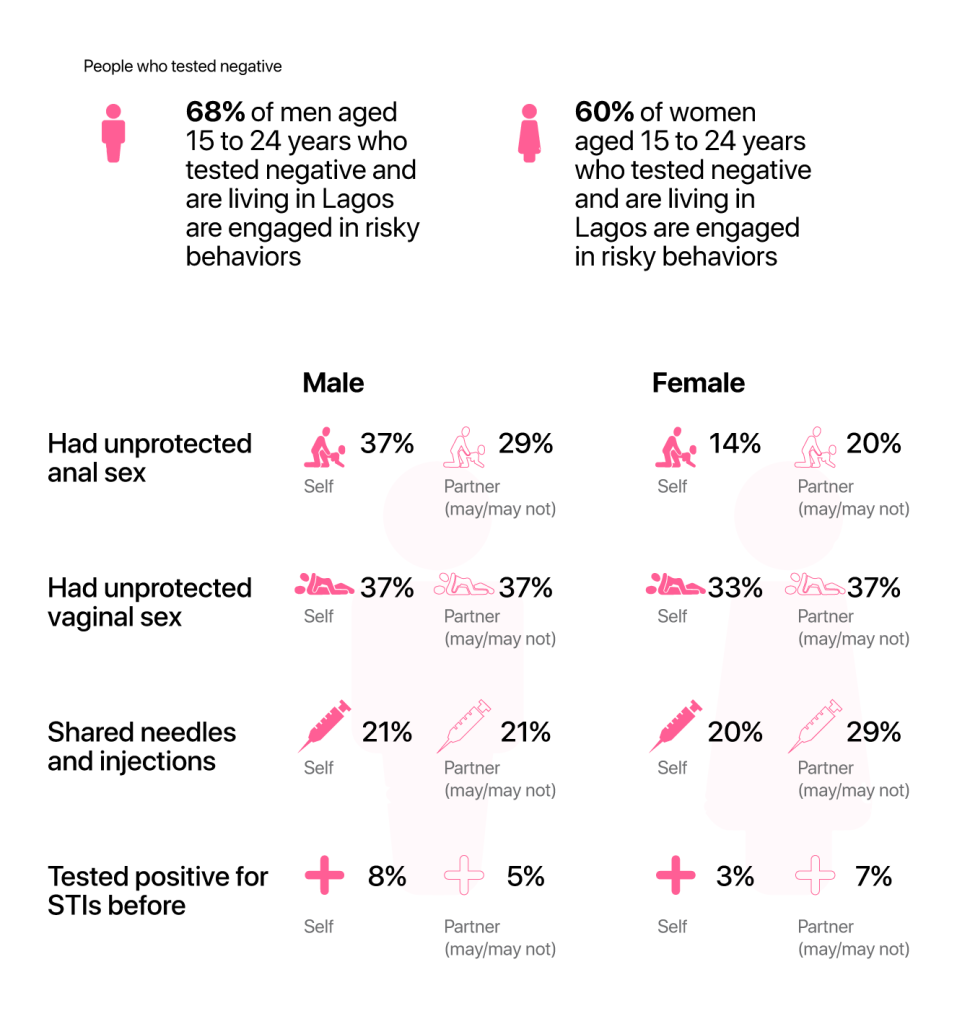
Risky Behaviour
Conclusion
Results obtained from tests submitted on itest revealed that HIV prevalence in Lagos is 2.2% among Nigerian self-testers aged 15-24 years. Male youth are more than twice as likely to be living with HIV than females [4.2% versus 1.8%], whereas Nigeria’s national HIV prevalence in the same group (15-24 years) is 0.65%, and women are 60% more likely to be living with HIV than men [0.8% versus 0.5%] (World Bank Group, 2018). The highest prevalence of HIV is found in adults aged 15 to 19 years (3.1%).
Despite their elevated risk, reports show that few adolescents test for HIV regularly. In 2017 only 2% of males between 15 and 19 and 4% of females had tested for HIV in the last 12 months (Unicef, 2017). The national targets by 2020 for young people are 90% for treatment and 50% for testing (NACA, 2015). Given the high proportion of young people in Lagos who are currently HIV negative, there is a need to do more sensitization on some of these risky behaviours. More also needs to be done to encourage young people to test for HIV regularly. We hope to see this with tools like iTest.