Background
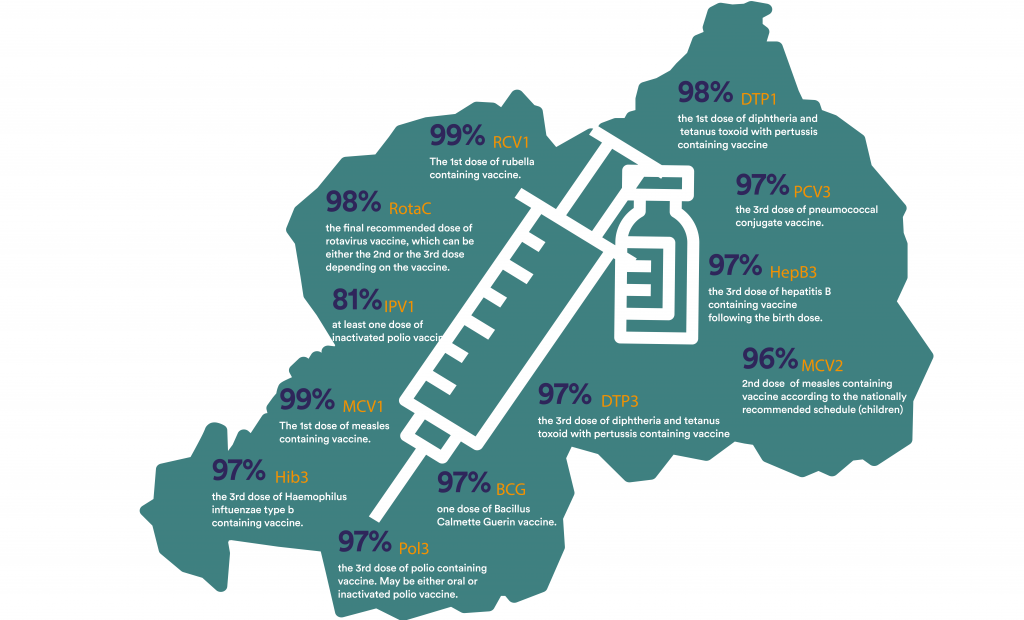
The community is protected when everyone gets immunized. If not, diseases spread those not immunized. In Rwanda, at least 4 children are born per woman, according to the latest population and housing census, Rwanda (2012). Among these babies more than 95% receive all recommended vaccines before 23 months old. These are the highest immunization coverage rates in sub-Saharan Africa.
Rwanda had pulled many of its resources to fight against preventable diseases. In the years that followed the genocide, more than one in four children would die of preventable causes before 5 yrs. The coverage of most WHO-recommended immunizations then were below 25%. Through regional and international partnerships such as GAVI, Rwanda has been able to sustain a vaccination coverage of at least 96% for the most common vaccines.
The increase in coverage rates has massively contributed to reducing infant mortality rate from 177 deaths per 1000 live births in 1998 to 27 deaths per 1000 live births in 2018.
Immunization Coverage Over the Years
According to the world’s biggest survey on public attitudes toward health and science, around 8 in 10 people agree vaccines are safe and Rwanda has the highest level of trust in vaccines globally. The graph below is brings to perspective the Rwandan immunization coverage (use drop down to select a specific vaccine).
Our data source is WHO/UNICEF coverage estimates for 2000-2018, as of 1 July 2019. For more detailed information on estimates methods is available here.
How do they do it?
Generally, immunization coverage rates for the WHO-recommended vaccines in Rwanda have been relatively high since 2009. Consistently being higher than aggregated global estimates. The attainment of remarkable coverage rates in the most common vaccines in Rwanda mainly due to:
- Involvement of community-based health workers. The CHWs sensitize people in their communities and ensure that every child within their community is immunized. More emphasis is also put on reaching vulnerable populations.
- The integration of technology in health sector has also contributed massively. Computer based trackers such as the immunization in-tracker are in used.
- Regular training and appraisal of staff involved in immunization keeps the staff motivated. Concrete measures are currently being taken to reach any missed children and maintain the high coverage in a cost effective and sustainable ways.
CcHUB Design Lab held a boot camp for the 2019/2020 Design Trainees. The boot-camp exercises involved exploring Rwanda’s immunization challenges. Read about their experiences here.

